(class)
Encloses a Graphic in a box with scrollbars.
Example
The simplest use of a
ScrollBox consists simply of providing the child
Graphic as an argument when creating the
ScrollBox:
| Example |
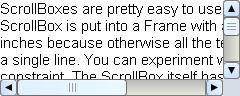 |
{ScrollBox
width = 2.5in, height = 1in,
{Frame
width = 4in,
{paragraph
ScrollBoxes are pretty easy to use. The text
in this ScrollBox is put into a Frame with a
specified width of 4 inches because otherwise
all the text would spread out on a single
line. You can experiment with changing this
width constraint. The ScrollBox itself has a
specified width and height because otherwise
it would size itself at its preferred size,
which is the preferred size of its contents.
The way this example is set up, you will be
able to see scrolling actually happening, but
if you want to see the effect of changing or
removing the specified height and width
constraints, you can do that too.
}
}
}
| |
Notes
This object can be styled by writing style rules for "ScrollBox".
| constructor public | {ScrollBox.default viewport-class:Type = Viewport, ...} |
local option public ScrollBox.accept-focus?:
bool =true
local option public ScrollBox.always-disable-hscroll?:
bool =false
local option public ScrollBox.always-disable-vscroll?:
bool =false
| expanded-hscroll-bounds?: | Expand the scrollable region horizontally so that the contents can be scrolled just out of view. |
local option public ScrollBox.expanded-hscroll-bounds?:
bool =false
local option public ScrollBox.expanded-vscroll-bounds?:
bool =false
nonlocal option public ScrollBox.focus-manager:#
FocusManager accessor public ScrollBox.have-hscroll?:
bool accessor public ScrollBox.have-vscroll?:
bool | hblocksize: | Specifies the horizontal distance covered by block scrolling. |
local option public ScrollBox.hblocksize:
Distance =0m
accessor public ScrollBox.horizontal-position:
Distance setter public ScrollBox.horizontal-position:
Distance local option public ScrollBox.hscroll-quantized?:
bool =false
| hscroll?: | Enables/Disables scrolling in the horizontal direction. Its default is true. |
local option public ScrollBox.hscroll?:
bool =true
| hunitsize: | Specify the horizontal distance covered by the unit scrolling gesture. |
local option public ScrollBox.hunitsize:
Distance =0m
accessor public ScrollBox.max-horizontal-position:
Distance accessor public ScrollBox.max-vertical-position:
Distance accessor public ScrollBox.min-horizontal-position:
Distance accessor public ScrollBox.min-vertical-position:
Distance local option public ScrollBox.reserve-corner?:
bool =false
local option public ScrollBox.shrink-hscroll?:
bool =true
local option public ScrollBox.shrink-vscroll?:
bool =true
accessor public ScrollBox.style-element:
String local option public ScrollBox.take-focus?:
bool =false
| vblocksize: | Specifies the vertical distance covered by the block scrolling gesture. |
local option public ScrollBox.vblocksize:
Distance =0m
accessor public ScrollBox.vertical-position:
Distance setter public ScrollBox.vertical-position:
Distance local option public ScrollBox.vscroll-quantized?:
bool =false
| vscroll?: | Enables/Disables scrolling in the vertical direction. It is by default true. |
local option public ScrollBox.vscroll?:
bool =true
| vunitsize: | Specify the vertical distance covered by the unit scrolling gesture. |
local option public ScrollBox.vunitsize:
Distance =0m
Properties inherited from Graphic:
avoid-page-break?, background, border-color, border-spec, border-style, border-width, cell-border-spec, cell-border-width, cell-margin, discrete-select-in-range?, enabled?, graphic-selectable, height, horigin, is-paginating?, layout, margin, opaque-to-events?, option-parent, outside-margin, pagination-state, parent, possibly-displayed?, selection-context, shadow-color, shadow-spec, visible?, visual-parent, vorigin, width Properties inherited from Visual:
_style-element, cursor, data-source, dragee, font-size, graphical-parent, has-key-focus?, input-method-enabled?, input-method-keyboard-mode, name, options, style-class, style-manager, style-options, test-child?, test-description, test-name, test-parent?, test-type-name, test-visible?, tooltip, user-data
| public | {ScrollBox.constrain-height}:Dimension |
| protected | {ScrollBox.create-hscroll}:Scrollbar |
| protected | {ScrollBox.create-main-panel}:Graphic |
| protected | {ScrollBox.create-vscroll}:Scrollbar |
| public | {ScrollBox.descendant-suggests-key-focus-request}:void |
| public | {ScrollBox.end-pagination}:void |
| public | {ScrollBox.make-gui-mark}:GuiMark |
| public | {ScrollBox.paginate}:(PaginationState, PaginationQuality) |
| public | {ScrollBox.scroll-to-include-relative-point}:void |
| scroll-to-object: | Position the viewport of a ScrollBox so that the top left corner of a given object coincides with the top left corner of the viewport. |
| public | {ScrollBox.scroll-to-object}:void |
| public | {ScrollBox.set-scroll-sizes view-bounds:GRect}:void |
| set-size: | Assigns this object its layout width and height. |
Methods inherited from BaseFrame:
add-internal, after-reposition, allocate-layout-object, attempt-revalidate-layout, before-reposition, compute-child-bounds, compute-parent-elastic, draw, get-text, install-child-bounds, internal-remove-child, note-attached, note-detaching, notify-option-children, pick-child, propagate-request-layout, register-options Methods inherited from Graphic:
create-pagination-state, detach, draw-range-as-selected, draw-shadow, find-ancestor, find-graphical-ancestor, fire-inferior-crossing-event, get-graphical-root, get-gui-path, get-origin-in-graphical-ancestor, get-origin-in-root, get-pagination-state, get-top-left-in-ancestor, get-visible-bounds-into, on-drag-enter, on-inspection, on-pointer-enter, option-changed, paint-with-decorations, replace-with, request-draw, request-draw-rect, request-pointer-trace, search-next, search-prev, set-layout, start-pagination, xy-offset-to Methods inherited from Visual:
add-from-init-args, animate, change-cursor, clonable-appearance?, clone-appearance, get-focus-manager, get-layout-context, get-test-parent, get-test-property, get-view, maybe-fire-attach-event, maybe-fire-detach-event, non-keyword-init-arg, note-caret-position, on-drag-leave, on-pointer-leave, pop-cursor, prepare-test-object, prepare-test-parent, push-cursor, quantize-width, refresh-style-options, release-key-focus, request-key-focus, scroll-to-include, test-record, test-run, transform-from-display-coordinates, transform-from-graphical-root-coordinates, transform-to-display-coordinates, transform-to-graphical-root-coordinates Methods inherited from GuiEventTarget:
handle-delegate-event, handle-event, on-action, on-cancel-mode, on-command-changed, on-commit, on-composition-change-event, on-composition-result-event, on-context-menu-event, on-current-record-change-request, on-current-record-changed, on-destroy-notify, on-destroy-requested, on-drag-pointer, on-drag-started, on-drop, on-end-composition-event, on-focus-event, on-focus-in, on-focus-out, on-gesture, on-gesture-magnify, on-gesture-rotate, on-gesture-swipe, on-gesture-tap, on-gesture-touch, on-grab-release, on-gui-event, on-input-method-event, on-key-event, on-pointer-button, on-pointer-crossing, on-pointer-event, on-pointer-motion, on-pointer-release, on-raw-key-event, on-raw-key-press, on-raw-key-release, on-reset, on-selectable-added, on-selectable-removed, on-selection-changed, on-selection-context-activated, on-selection-context-deactivated, on-selection-event, on-start-composition-event, on-start-event, on-stop-event, on-view-activate, on-view-deactivate, on-window-close, remove-event-handlers-for-event-class Methods inherited from OptionListInterface:
add-option, add-style-option, change-option-parent-notify, clone-options, get-option, get-option-by-name, keyword-init-arg, local-add-notify, local-remove-notify, name-to-option-key, new-option-item, option-change-notify, option-lookup, option-lookup-here, option-propagate-notify, option-set?, propagate-option-change, remove-option, remove-style-option, remove-styles, set-option-by-name, set-style-option-by-name, unset-option-by-name, unset-style-option-by-name
(constructor)
| public | {ScrollBox.default viewport-class:Type = Viewport, ...} |
Initialize a new ScrollBox.
viewport-class: Indicates the type of the object that should be created to serve as the
ScrollBox's viewport. If this argument is supplied, its value must be a class type that is
Viewport or a subclass of
Viewport.
...: Additional arguments to this constructor are the same as the arguments that can be supplied to the default
Frame constructor.
Notes
(local option)
public ScrollBox.accept-focus?:
bool =true
Control whether a ScrollBox will accept the keyboard focus.
Description
(local option)
public ScrollBox.always-disable-hscroll?:
bool =false
Force the horizontal Scrollbar to be disabled.
Description
When true, the horizontal
Scrollbar will act as if it were not needed, even if it is. The reason this option exists is that the
ScrollBox's layout decisions are affected by the
ScrollBox.hscroll? option. Typically, this is the desired effect, but there are times in which one might want the
hscroll?=true layout rules but not have a
Scrollbar; this can be accomplished by setting
always-disable-hscroll? = true, shrink-hscroll? = true.
| shrink-hscroll? | always-disable-hscroll? |
|---|
| false | false | Always show the horizontal Scrollbar. |
| true | false | Show the horizontal Scrollbar only when needed. |
| true | true | Never show the horizontal Scrollbar. |
| false | true | Show a disabled horizontal Scrollbar. |
See also
ScrollBox.shrink-hscroll?.
Example
Try various combinations of always-disable-hscroll? and shrink-hscroll?.
| Example |
 |
{ScrollBox
width = 2in, height = 1in, background = "lime",
shrink-hscroll? = true, always-disable-hscroll? = true,
{RectangleGraphic
width = 5in, height = 5in, background = "yellow"
}
}
| |
(local option)
public ScrollBox.always-disable-vscroll?:
bool =false
Force the vertical Scrollbar to be disabled.
Description
When true, the vertical
Scrollbar will act as if it were not needed, even if it is. The reason this option exists is that the
ScrollBox's layout decisions are affected by the
ScrollBox.vscroll? option. Typically, this is the desired effect, but there are times in which one might want the
vscroll?=true layout rules but not have a
Scrollbar; this can be accomplished by setting
always-disable-vscroll? = true, shrink-vscroll? = true.
| shrink-vscroll? | always-disable-vscroll? |
|---|
| false | false | Always show the vertical Scrollbar. |
| true | false | Show the vertical Scrollbar only when needed. |
| true | true | Never show the vertical Scrollbar. |
| false | true | Show a disabled vertical Scrollbar. |
See also
ScrollBox.shrink-vscroll?.
Example
Try various combinations of always-disable-vscroll? and shrink-vscroll?.
| Example |
 |
{ScrollBox
width = 2in, height = 1in, background = "lime",
shrink-vscroll? = true, always-disable-vscroll? = true,
{RectangleGraphic
width = 5in, height = 5in, background = "yellow"
}
}
| |
(nonlocal option)
The DisplayContext associated with this object.
Programming Notes
This option is used for communication purposes within the Curl graphics system. It should not be casually set or unset by user code. It should also not usually be read directly by user code: if you want the current
DisplayContext, you should fetch it by calling
Visual.get-display-context.
Every graphic hierarchy that can be displayed, whether in a window on the screen or on a printed page, must have at its root an object that sets the
display-context option to a
DisplayContext object that is suitable for the display medium by means of which the graphic hierarchy will be seen. Thus, an object can tell that it has been attached to a displayable graphic hierarchy by watching for the
display-context option's value to change from
null to a non-
null DisplayContext object. Accordingly, subclasses of
Visual that need to take specific actions when they become connected to a displayable graphic hierarchy monitor the
display-context option by including an option declaration such as
{nonlocal-option public display-context:#DisplayContext
change handler}where the code in
change handler looks at the current value of the
display-context option (available within the change handler as the value of the variable
display-context), watching for changes between
null and non-
null values, and takes any actions that are needed.
Programmers using this programming idiom should be aware, however, that it is fairly common when rearranging graphical displays to detach graphical objects temporarily from a graphic hierarchy and then reattach them to the same hierarchy, which will cause the detached objects to temporarily see the
display-context object become
null and then become non-
null again. Code that monitors changes in the
display-context option should take this possibility into account and avoid taking undesired actions in this case.
(local option)
public ScrollBox.expanded-hscroll-bounds?:
bool =false
Expand the scrollable region horizontally so that the contents can be scrolled just out of view.
Description
When false, the scroll bounds are such that the bounds of the contents define the scrolling region. When true, the scroll bounds also include the region just outside of these bounds, up to the point where the contents have just scrolled out of view.
Example
| Example |
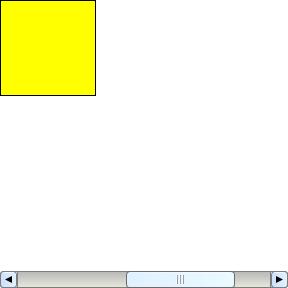 |
{ScrollBox
height = 3in, width = 3in, expanded-hscroll-bounds? = true,
{RectangleGraphic width = 1in, height = 1in}
}
| |
Notes
By default, this is false.
(local option)
public ScrollBox.expanded-vscroll-bounds?:
bool =false
Expand the scrollable region vertically so that the contents can be scrolled just out of view.
Description
When false, the scroll bounds are such that the bounds of the contents define the scrolling region. When true, the scroll bounds also include the region just outside of these bounds, up to the point where the contents have just scrolled out of view.
Example
| Example |
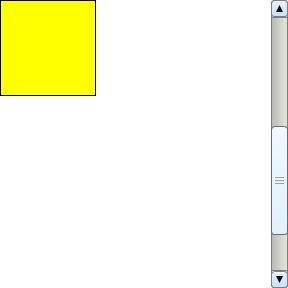 |
{ScrollBox
height = 3in, width = 3in, expanded-vscroll-bounds? = true,
{RectangleGraphic width = 1in, height = 1in}
}
| |
Notes
By default, this is false.
(nonlocal option)
The FocusManager associated with this object.
Notes
This option is used for communication purposes within the Curl graphics system. It should not be casually set or unset by user code. It should also not be read directly by user code: if you want the current
FocusManager, you should fetch it by calling
Visual.get-focus-manager.
(accessor)
accessor public ScrollBox.have-hscroll?:
bool Indicates whether this ViewportBox can have its horizontal scroll position modified.
Description
have-hscroll? indicates that horizontal scrolling may be required; e.g., because the
Viewport's contents are larger than the
Viewport.
One would typically expect that
have-hscroll? would always be false when
hscroll? was false, but this it not a requirement.
Notes
This value differs from
ScrollBox.hscroll?, which indicates whether the
ScrollBox should lay out its contents such that horizontal scrolling might be required.
Overriding
The default implementation
ViewportBox.have-hscroll? always returns true. Subclasses can override this method to return false in situations that call for it.
(accessor)
accessor public ScrollBox.have-vscroll?:
bool Indicates whether this ViewportBox can have its vertical scroll position modified.
Description
have-vscroll? indicates that vertical scrolling may be required, for example, because the
Viewport's contents are larger than the
Viewport.
One would typically expect that when
vscroll? is false,
have-vscroll? would always be false, but this is not a requirement.
Notes
This value differs from
ScrollBox.vscroll?, which indicates whether the
ScrollBox should lay out its contents such that vertical scrolling might be required.
Overriding
The default implementation
ViewportBox.have-vscroll? always returns true. Subclasses can override this method to return false in situations that call for it.
(local option)
public ScrollBox.hblocksize:
Distance =0m
Specifies the horizontal distance covered by block scrolling.
Description
The value of this option specifies the amount by which the contents of this
ScrollBox should move horizontally when the user performs block scrolling.
When the value of this option is
0m, the block scrolling distance will be 90% of the width of the viewport inside of the
ScrollBox. (In other words, by default there is a 10% overlap between the viewport contents before and after the block scrolling gesture is made.)
This default distance will be further adjusted so that it is an integer multiple of the horizontal
unit scrolling distance. (If the block scrolling gesture is made at a time when the remaining available scrolling distance is less than the block scrolling distance, then the scrollbar moves by the total amount of the remaining available scrolling distance.)
It is an error to set this option to a
Distance less than
0m.
(accessor)
accessor public ScrollBox.horizontal-position:
Distance setter public ScrollBox.horizontal-position:
Distance The current horizontal position.
Overriding
(local option)
public ScrollBox.hscroll-quantized?:
bool =false
Control the Scrollbar.quantized? option of a ScrollBox's horizontal Scrollbar.
Description
Setting this option forces the horizontal Scrollbar's value to always be constrained to integer multiples of its unit scrolling distance.
(local option)
public ScrollBox.hscroll?:
bool =true
Enables/Disables scrolling in the horizontal direction. Its default is true.
Description
Setting
hscroll? option to
false does not merely hide the horizontal
Scrollbar. The
Scrollbar is actually eliminated and no scrolling occurs in the horizontal direction. This results in the contents of the
ScrollBox getting squished in the horizontal direction if there is not enough space for the contents in this direction.
(local option)
Specify the horizontal distance covered by the unit scrolling gesture.
Description
The value of this option specifies the amount by which the contents of this
ScrollBox should move horizontally when the user performs unit scrolling.
When the value of this option is
0m, the unit scrolling distance will be calculated dynamically. In particular, it will be one-tenth of the block scrolling distance. (Note that the block scrolling distance may also be calculated dynamically.)
It is an error to set this option to a
Distance less than
0m.
(accessor)
accessor public ScrollBox.max-horizontal-position:
Distance The maximum horizontal position.
Description
(accessor)
accessor public ScrollBox.max-vertical-position:
Distance The maximum vertical position.
Description
(accessor)
accessor public ScrollBox.min-horizontal-position:
Distance The minimum horizontal position.
Description
(accessor)
accessor public ScrollBox.min-vertical-position:
Distance The minimum vertical position.
Description
(local option)
public ScrollBox.reserve-corner?:
bool =false
Reserves the bottom right corner of the ScrollBox.
Notes
If
true, the bottom right corner of the
ScrollBox will have a
Graphic if one or more
Scrollbars of this object is showing.
Notes
This is generally used on the Mac OS X™ platform by
ScrollBoxs that are used as containers by a
View. Not making a
ScrollBox reserve the corner space will have an annoying problem of not been able to use the buttons of the
Scrollbox as that space is used by the operating system for resizing the
View's window.
Introduced in:
version 6.0
(local option)
public ScrollBox.shrink-hscroll?:
bool =true
Control whether a ScrollBox's horizontal Scrollbar vanishes when it is not needed.
Description
If this option is set to true (the default), the horizontal
Scrollbar vanishes when it is not needed. If the option is set to false, the
Scrollbar continues to occupy the same amount of space but is drawn as disabled when it is not needed.
See also
ScrollBox.always-disable-hscroll?.
(local option)
public ScrollBox.shrink-vscroll?:
bool =true
Control whether a ScrollBox's vertical Scrollbar vanishes when it is not needed.
Description
If this option is set to true (the default), the vertical
Scrollbar vanishes when it is not needed. If the option is set to false, the
Scrollbar continues to occupy the same amount of space but is drawn as disabled when it is not needed.
See also
ScrollBox.always-disable-vscroll?.
(accessor)
accessor public ScrollBox.style-element:
String The "element" or "type" of this Visual, for the purpose of styling.
Description
This implementation returns the value of
Visual._style-element but is normally overridden to return a constant value.
Overriding
If a subclass of
Visual should be stylable separately from other types of objects, this getter should be overridden to return an appropriate string. By convention, this string is the name of the class or the name of the markup that produces the object.
An override must return
self._style-element if it is not the empty string.
Introduced in:
version 6.0
(local option)
public ScrollBox.take-focus?:
bool =false
Control whether a ScrollBox initially requests the keyboard focus.
Description
If the value of this option is true, then this
ScrollBox will request the keyboard focus whenever it is attached to a
FocusManager. Otherwise, the
ScrollBox will request the keyboard focus only when the user clicks on one of the scrollbars or clicks inside the
ScrollBox on some object that does not consume the pointer-click event. See also
ScrollBox.accept-focus?.
(local option)
public ScrollBox.vblocksize:
Distance =0m
Specifies the vertical distance covered by the block scrolling gesture.
Description
The value of this option specifies the amount by which the contents of this
ScrollBox should move vertically when the user performs block scrolling.
When the value of this option is
0m, the block scrolling distance will be 90% of the height of the viewport inside of the
ScrollBox. (In other words, by default there is a 10% overlap between the viewport contents before and after the block scrolling gesture is made.)
This default distance will be further adjusted so that it is an integer multiple of the vertical
unit scrolling distance. (If the block scrolling gesture is made at a time when the remaining available scrolling distance is less than the block scrolling distance, then the scrollbar moves by the total amount of the remaining available scrolling distance.)
It is an error to set this option to a
Distance less than
0m.
(accessor)
accessor public ScrollBox.vertical-position:
Distance setter public ScrollBox.vertical-position:
Distance The current vertical position.
Overriding
(local option)
public ScrollBox.vscroll-quantized?:
bool =false
Control the Scrollbar.quantized? option of a ScrollBox's vertical Scrollbar.
Description
Setting this option forces the vertical Scrollbar's value to always be constrained to integer multiples of its unit scrolling distance.
(local option)
public ScrollBox.vscroll?:
bool =true
Enables/Disables scrolling in the vertical direction. It is by default true.
Description
Setting
vscroll? option to
false does not merely hide the vertical
Scrollbar. The
Scrollbar is actually eliminated and no scrolling occurs in the vertical direction. This results in the contents of the
ScrollBox getting squished in the vertical direction if there is not enough space for the contents in this direction.
(local option)
Specify the vertical distance covered by the unit scrolling gesture.
Description
The value of this option specifies the amount by which the contents of this
ScrollBox should move vertically when the user performs unit scrolling.
When the value of this option is
0m, the unit scrolling distance will be calculated dynamically. In particular, it will be one-tenth of the block scrolling distance. (Note that the block scrolling distance may also be calculated dynamically.)
It is an error to set this option to a
Distance less than
0m.
(method)
| public | {ScrollBox.constrain-height}:Dimension |
Return the width preference of this Graphic when subjected to a specified height constraint.
ascent, descent: the height constraint, expressed as ascent and descent distances relative to the origin of this
Graphic.
Returns
Overriding
The default method
Graphic.constrain-height simply invokes
Graphic.get-width-preference. This method need not be overridden unless an object needs to take the height constraint into account in computing its width preference.
Classes overriding this method should take care to return a
Dimension which represents the space along the horizontal axis which is required,
including how it relates to their object's origin. In practice, this means that this method should return either an appropriate
OriginElastic, or a
Dimension which will be converted to an appropriate
OriginElastic via the conversion rules described in
Converting Dimensions to OriginElastics.
Important note: Any overriding implementation of this method must include a call to the superclass implementation in order to insure that the layout negotiation is propagated appropriately throughout the entire graphical hierarchy.
(method)
Return the height preference of this Graphic when subjected to a specified width constraint.
lextent, rextent: the width constraint, expressed as distances to the left and right relative to the origin.
Returns
Overriding
The default method
Graphic.constrain-width simply invokes
Graphic.get-height-preference. This method need not be overridden unless an object needs to take the width constraint into account in computing its height preference.
Classes overriding this method should take care to return a
Dimension which represents the space along the vertical axis which is required,
including how it relates to their object's origin. In practice, this means that this method should return either an appropriate
OriginElastic, or a
Dimension which will be converted to an appropriate
OriginElastic via the conversion rules described in
Converting Dimensions to OriginElastics.
Important note: Any overriding implementation of this method must include a call to the superclass implementation in order to insure that the layout negotiation is propagated appropriately throughout the entire graphical hierarchy.
(method)
| protected | {ScrollBox.create-hscroll}:Scrollbar |
Create a Scrollbar to be used for the horizontal scrolling in the ScrollBox.
Notes
This is called by the constructor of the ScrollBox.
Various properties and event handlers will be set to this Scrollbar to make it suitable for horizontal scrolling.
Introduced in:
version 6.0
(method)
| protected | {ScrollBox.create-main-panel}:Graphic |
Creates the user interface for the ScrollBox.
Returns
The
Graphic that will be used for the user interface of the
ScrollBox.
Description
This is called by the constructor of the
ScrollBox after setting and initializing the vertical and the horizontal
Scrollbar's.
By default, this method arranges the vertical and the horizontal
Scrollbar's and the
Viewport to provide the user interface for the
ScrollBox.
Introduced in:
version 6.0
(method)
| protected | {ScrollBox.create-vscroll}:Scrollbar |
Create a Scrollbar to be used for the vertical scrolling in the ScrollBox.
Notes
This is called by the constructor if a Scrollbox.
Various properties and event handlers will be set to this Scrollbar to make it suitable for vertical scrolling.
Introduced in:
version 6.0
(method)
| public | {ScrollBox.descendant-suggests-key-focus-request}:void |
A means by which the contents of a ScrollBox can indicate that it should request the keyboard focus.
Notes
(method)
| public | {ScrollBox.end-pagination}:void |
Ends the pagination process for this Graphic and deallocates data structures for recording the PaginationState.
Programming Notes
Notes
(method)
Return the height preference of this Graphic.
Returns
Overriding
This method must be defined in a subclass of
Graphic.
Classes overriding this method should take care to return a
Dimension which represents the space along the vertical axis which is desired,
including how it relates to their object's origin. In practice, this means that this method should return either an appropriate
OriginElastic, or a
Dimension which will be converted to an appropriate
OriginElastic via the conversion rules described in
Converting Dimensions to OriginElastics.
(method)
Get the horizontal Scrollbar associated with this ScrollBox.
Returns
The horizontal Scrollbar.
Notes
When used as part of a
ScrollBox, certain aspects of the
Scrollbar are under the
ScrollBoxes control. For example, the following options may be set by the
ScrollBox at any time:
In addition, the
ScrollBox assumes that the value for these and other options (
direction, in particular) will not otherwise be modified on the
Scrollbar.
These lists of sensitive options may change in the future. In general, one should not manipulate a
Scrollbar directly if it came from a
ScrollBox.
(method)
Get the vertical Scrollbar associated with this ScrollBox.
Returns
The vertical Scrollbar.
Notes
When used as part of a
ScrollBox, certain aspects of the
Scrollbar are under the
ScrollBoxes control. For example, the following options may be set by the
ScrollBox at any time:
In addition, the
ScrollBox assumes that the value for these and other options (
direction, in particular) will not otherwise be modified on the
Scrollbar.
These lists of sensitive options may change in the future. In general, one should not manipulate a
Scrollbar directly if it came from a
ScrollBox.
(method)
Return the width preference of this Graphic.
Returns
Overriding
This method must be defined in a subclass of
Graphic.
Classes overriding this method should take care to return a
Dimension which represents the space along the horizontal axis which is desired,
including how it relates to their object's origin. In practice, this means that this method should return either an appropriate
OriginElastic, or a
Dimension which will be converted to an appropriate
OriginElastic via the conversion rules described in
Converting Dimensions to OriginElastics
(method)
| public | {ScrollBox.make-gui-mark}:GuiMark |
The standard way to create a GuiMark referencing this Graphic.
Returns
A newly allocated GuiMark initialized to the leading edge of the Graphic.
Overriding
Subclasses of Graphics which require custom subclasses of GuiMark to refer to their contents should override this method.
(method)
The static event handler for DragOver events.
Description
(method)
The static event handler for GestureBegin events.
Description
A
ScrollBox can scroll via
GestureEvents on systems with appropriate hardware and operating system support. To enable this for any given
ScrollBox, have that
ScrollBox grab the pointer before this method is called; e.g. either by overriding this method or adding a dynamic event handler calling
GestureBegin.continue-implicit-pointer-grab with the
ScrollBox as the target. The
GestureBegin will be consumed if this method causes the
ScrollBox to accept future
GesturePan events for scrolling.
See
GuiEventTarget.on-pointer-event for general information about
static event handlers.
Introduced in:
version 8.0
(method)
The static event handler for GestureEnd events.
Description
Introduced in:
version 8.0
(method)
The static event handler for GesturePan events.
Description
Introduced in:
version 8.0
(method)
The static event handler for KeyPress events.
Description
(method)
The static event handler for PointerPress events.
Description
(method)
(method)
| public | {ScrollBox.paginate}:(PaginationState, PaginationQuality) |
Paginate the graphic.
page-height: The height available to render the graphic on the page. This does not include the space taken up by border and margin.
next-page-height: The height that would be available to paginate this graphic if this graphic was moved to the next page.
Returns
The returned
PaginationState is the pagination state of the
Graphic after this method is called.
The returned
PaginationQuality value describes the quality of the page split that will be achieved using the given
page-height.
Programming Notes
Before paginating a
Graphic one may call this function with
query-only? set to
true. In this way the caller can determine what
PaginationQuality can be achieved with the given
page-height. Depending on the
PaginationQuality, the caller can decide to paginate a portion on an object in the current page or push it entirely to the next page by setting the
PaginationState.end-offset of the
PaginationState associated to the
Graphic to point to the top of this object.
Overriding
Override this method if you want a
Graphic to paginate itself across pages in some specific way.
You should follow these rules when overriding this method:
Call
Graphic.get-pagination-state with
query-only? to get the current pagination state of this
Graphic. When
query-only? is
true, the method acts on a clone of the
PaginationState of this
Graphic.
If this methods is called on a
Graphic that previously returned PaginationQuality.complete then make sure that the
PaginationState.start-offset is set to
PaginationState.end-offset and the returned pagination quality is
PaginationQuality.complete.
If the
page-height is negative or negligible then the returned pagination state should be the current pagination state of the object and the returned pagination quality must be
PaginationQuality.clipped-outside.
Otherwise, given the available
page-height now compute and set the
PaginationState.start-offset,
PaginationState.end-offset, and
PaginationState.min-end-offset for the new page and return the appropriate
PaginationQuality for this pagination sequence.
A container, like a
Box, if paginating should try not to split its children across pages. If the container cannot fit a child in the current page then it should follow the following two steps.
1. It should see if its child has requested to avoid page breaks (see
Graphic.avoid-page-break?). If it did, then it should push it to the next page,if the height available for this graphic in the current page is lesser than
next-page-height. To push the child to the next page the container has to set the
PaginationState.end-offset of its current
PaginationState to the top of the child which is
-{child.get-cell-bounds}.ascent.
2. Ask the child to paginate and if the returned
PaginationQuality is
PaginationQuality.good or better then start the child's pagination in the current page. Otherwise the container should try to determine if the child's pagination would be at least
PaginationQuality.good if it pushes it to the next page by calling the
Graphic.paginate method with
query-only? passed as
true and
page-height and
next-page-height passed as
next-page-height that was passed to its own
Graphic.paginate method. If yes, then it should push it to the next page otherwise make the child paginate from the current page.
Note that a container should ask the
Layout of its child graphic to paginate, instead of the child graphic to paginate directly.
Here is some code that shows how a
Graphic.paginate is implemented.
{method public open {paginate
page-height:Distance,
next-page-height:Distance,
query-only?:bool
}:(PaginationState, PaginationQuality)
let pstate:PaginationState =
{self.get-pagination-state query-only?}
let bounds:GRect = pstate.bounds
let constant epsilon:Distance = epsilon-float * 1m
|| All done.
{if {abs bounds.descent - pstate.end-offset} < epsilon then
set pstate.start-offset = pstate.end-offset
{return pstate, PaginationQuality.complete}
}
|| No space left for the graphic.
{if page-height < epsilon then
{return pstate, PaginationQuality.clipped-outside}
}
let new-start-offset:Distance = pstate.min-end-offset
let new-end-offset:Distance =
{min new-start-offset + page-height, bounds.descent}
{return
{pstate.advance-pagination
new-start-offset,
new-end-offset,
quality-if-not-complete = PaginationQuality.poor
}
}
}
Notes
(method)
Positions the viewport of a ViewportBox as specified.
Notes
Invocation of this method will result in positioning the viewport, if possible, so that
ViewportBox.horizontal-position returns the value
x and
ViewportBox.vertical-position returns the value
y. If either
x or
y is not specified, then the current position of the viewport in that dimension is preserved.
Overriding
This abstract method of
ViewportBox must be overridden by concrete subclasses.
(method)
| public | {ScrollBox.scroll-to-include-relative-point}:void |
Set the scroll positions for this ScrollerInterfaces so that a specified point is visible.
relative-to: A
Visual defining the coordinate system in which
x and
y are based.
x, y: The point to be scrolled into view.
If either argument is not supplied, then no scrolling is performed in that direction.
min-window: Specifies the top and the left-hand bound of the region in the
ScrollerInterface's viewport where the specified point should appear.
min-window is a number between 0 and 1, specifying the fraction of the viewport's vertical extent that is above (and to the left of) the specified position. The default value is 0.
max-window: Specifies the bottom and the right-hand bound of the region in the
ScrollerInterface's viewport where the specified point should appear. Like
min-window,
max-window is a number between 0 and 1. Its default value is 1.
Overriding
Subclasses should comply with the description of this method as given in the documentation. If this is not possible, such as when a
ScrollerInterface is used to represent a positioning mechanism that doesn't involve
Visuals, then it is acceptable for subclasses to ignore the request.
(method)
| public | {ScrollBox.scroll-to-object}:void |
Position the viewport of a ScrollBox so that the top left corner of a given object coincides with the top left corner of the viewport.
g: The object of interest.
vertical-only?: Supply true for this argument to inhibit horizontal scrolling.
horizontal-only?: Supply true for this argument to inhibit vertical scrolling.
Notes
An error will be signaled if g is not a graphical descendant of this ScrollBox.
(method)
| public | {ScrollBox.set-scroll-sizes view-bounds:GRect}:void |
Sets the parameters of the ScrollBox after a change in the size of its Viewport or the object in the Viewport.
view-bounds: The new bounds of the Viewport.
Description
Performs the actions that a
ScrollBox needs to perform when there is a change in object sizes, such as adjusting the thumb length and range of values for any
Scrollbars.
Expected Events
Action: Fired by the
Scrollbox at itself after adjusting the parameters.
(method)
Assigns this object its layout width and height.
Description
When set-size is called on this object, it is assigned its layout size, and layout negotiation for it ends. Layout negotiation for a graphical hierarchy terminates after all graphic objects in the hierarchy have been assigned their layout size.
bounds: a
GRect indicating the left/right and up/down extents of this object's bounding box, relative to this object's origin.
Programming Notes
This method is invoked by the object's graphical parent.
Overriding
The default method
Graphic.set-size does nothing. Subclasses of
Graphic may override this method in order to intercept the information provided here.




